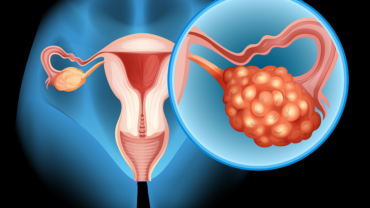
Uterine fibroids are harmless growths in the uterus that many women may not even realize they have. While they are incredibly common—affecting up to 70% of women by age 50—they often go unnoticed until they cause more serious symptoms. This makes understanding the silent signs of fibroids essential for women of all ages. By recognizing these subtle indications early, you can take proactive steps toward diagnosis and treatment.
What Are Uterine Fibroids?
Uterine fibroids, also known as leiomyomas or myomas, are non-cancerous growths made of muscle and fibrous tissue that develop in the uterus. They vary in size, from as small as a pea to as large as a melon, and can appear as a single growth or multiple growths in the uterus. While some women experience severe symptoms, others may have uterine fibroids that remain largely asymptomatic.
This means they often grow during reproductive years and may shrink after menopause. Risk factors include family history, age, obesity, and certain lifestyle habits.
Why Fibroids Can Be “Silent”
One of the most concerning aspects of fibroids is that many women don’t experience obvious symptoms. Some fibroids remain dormant for years, showing up only during routine exams or imaging tests. These are often the fibroids responsible for the subtle, yet important, silent signs of fibroids that women should never ignore.
Key Silent Signs of Fibroids
Even if you feel healthy, certain changes in your body may hint at the presence of fibroids.
1.Heavy Menstrual Bleeding
While heavy periods are often attributed to stress or hormonal changes, persistently heavy or prolonged bleeding may indicate uterine fibroids. Women might notice soaking through sanitary pads more frequently than usual or passing large clots during menstruation.
2. Pelvic Pressure or Pain
Fibroids can press against surrounding organs, causing a feeling of fullness, pressure, or dull pain in the lower abdomen or pelvic region. Some women experience backache, leg pain, or a dragging sensation, often mistaken for muscle strain or gastrointestinal issues.
3. Frequent Urination
Fibroids located near the bladder can increase urinary frequency or urgency. You may find yourself waking up multiple times at night to urinate or feeling a constant need to empty your bladder, even without increased fluid intake.
4. Bloating or Abdominal Swelling
Even small fibroids can cause noticeable changes in abdominal shape. Unexplained bloating, swelling, or a visible “baby bump” without pregnancy could be a subtle sign of fibroid growth.
5. Pain During Intercourse
Fibroids near the cervix or uterine wall can lead to discomfort or pain during sexual intercourse. This symptom is often underreported but can indicate the presence of uterine fibroids affecting reproductive health.
6. Unexplained Fatigue
Heavy menstrual bleeding associated with fibroids can lead to anemia, causing fatigue, dizziness, and weakness. This silent symptom is often dismissed as stress or lack of sleep, but it warrants a closer look.
7. Fertility Issues
Some fibroids can make it harder to get pregnant or increase the chances of having a miscarriage. Women experiencing difficulty in getting pregnant, particularly if no other underlying causes are identified, should discuss fibroids with their healthcare provider.
When to See a Doctor
While the silent signs of fibroids may seem minor, early evaluation is crucial.
- Menstrual cycles that suddenly become heavier or longer
- Pelvic pain or pressure that persists
- Changes in urinary or bowel habits
- Difficulty conceiving
Early detection allows for a range of treatment options, from medication to minimally invasive procedures or surgery, depending on the size, number, and location of the fibroids.
Diagnosis of Fibroids
Doctors typically diagnose fibroids using:
- Pelvic Examination: A physical check can sometimes reveal an enlarged or irregular uterus.
- Ultrasound: The most common imaging test to confirm fibroid presence.
- MRI: Provides detailed imaging, particularly for larger or complex fibroids.
- Hysteroscopy or Sonohysterography: Specialized tests for fibroids affecting the uterine cavity.
Treatment Options
Treatment depends on the severity of symptoms, fibroid size, and whether you plan to have children. Options include:
- Watchful Waiting: Small, asymptomatic fibroids may not require treatment but should be monitored.
- Medications: Hormonal treatments can help control bleeding and reduce fibroid size.
- Minimally Invasive Procedures: Uterine artery embolization or laparoscopic surgery can remove fibroids without major surgery.
- Surgical Options: Myomectomy removes fibroids while preserving the uterus, whereas hysterectomy removes the uterus entirely in severe cases.
Living with Fibroids
Lifestyle changes can complement medical treatments. Regular exercise, maintaining a healthy weight, and a balanced diet may help manage symptoms. Additionally, tracking your menstrual cycle and symptoms can provide valuable information to your healthcare provider.
The Takeaway
Awareness is the first step toward better health. The silent signs of fibroids may be easy to overlook, but recognizing them early can prevent complications and improve quality of life. Remember, not all fibroids cause severe symptoms, but subtle changes in your body should never be ignored.
If you suspect you might have fibroids or notice any of the signs mentioned above, schedule a consultation with a gynecologist. Understanding your body and taking proactive steps ensures that fibroids don’t silently affect your health.