Untreated Fibroids: What You Need to Know About Uterine Fibroids and Treatments
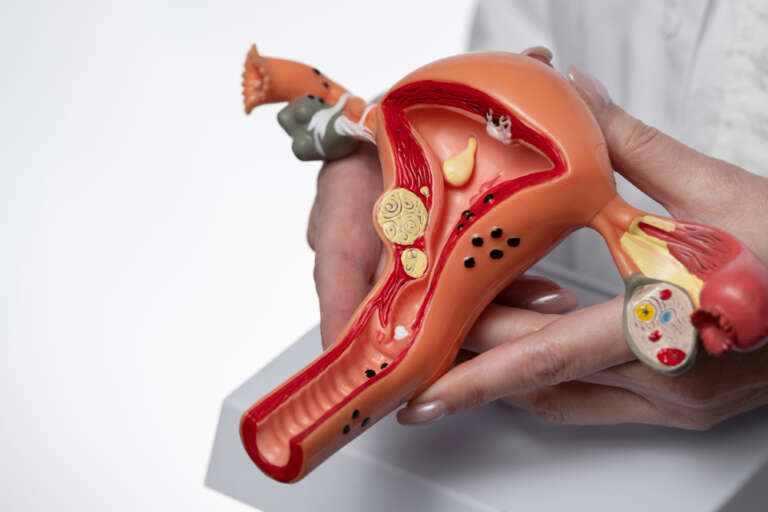
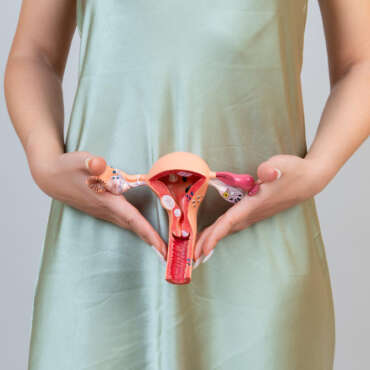
Uterine fibroids are non-cancerous growths that develop in or around the uterus, affecting millions of women worldwide. While some fibroids remain small and asymptomatic, others can grow significantly, causing discomfort and complications. Understanding uterine fibroids and the available treatments is crucial for maintaining reproductive health and overall well-being.
What Happens if You Do Not Treat Your Uterine Fibroids?
Many women may choose to ignore fibroids, especially if they do not experience symptoms. However, leaving fibroids untreated can lead to a range of complications over time.
In some cases, untreated fibroids can impact fertility, making it difficult to conceive or increasing the risk of miscarriage. Moreover, while most fibroids are benign, rarely, certain fibroids may undergo changes that require medical attention. Ignoring fibroids can also make future treatment more complicated, as larger fibroids often require more invasive procedures.
What Causes Uterine Fibroids?
These hormones stimulate the growth of uterine tissue, which can lead to fibroid formation.Genetic factors may also be involved.
Additionally, lifestyle factors such as obesity, diet, and vitamin D deficiency can increase the risk of fibroid development. Age is another factor, as fibroids are more common in women between 30 and 50 years old.
Symptoms of Uterine Fibroids
Symptoms of uterine fibroids can vary depending on the size, location, and number of fibroids. Many women remain asymptomatic, but common signs include:
> Heavy menstrual bleeding: This may lead to anemia and fatigue.
> Pelvic pain or pressure: Large fibroids can press on the bladder or bowel, causing discomfort.
> Frequent urination: Fibroids pressing on the bladder can result in increased urination.
> Pain during intercourse: Fibroids can make sexual activity uncomfortable or painful.
> Back or leg pain: Pressure from fibroids can sometimes radiate to the lower back or legs.
> Reproductive issues: Difficulty conceiving, recurrent miscarriages, or complications during pregnancy may occur.

Treatment of Fibroids
The treatment of uterine fibroids depends on the severity of symptoms, fibroid size, location, and the patient’s reproductive goals. Not all fibroids require treatment, especially if they are small and asymptomatic.
1. Medications:
Medications can help manage symptoms but do not eliminate fibroids. Options include hormonal treatments, such as birth control pills or gonadotropin-releasing hormone (GnRH) agonists, which can shrink fibroids and control heavy bleeding.
2. Minimally Invasive Procedures:
> Uterine artery embolization (UAE): Cuts off blood supply to fibroids, causing them to shrink.
> MRI-guided focused ultrasound: Uses high-frequency sound waves to destroy fibroid tissue.
3.Surgical Options:
> Myomectomy: Surgical removal of fibroids, preserving the uterus for future pregnancies.
> Hysterectomy: Complete removal of the uterus, which is a definitive treatment for fibroids, often recommended when other treatments fail.
4. Lifestyle and Home Remedies:
Although lifestyle changes cannot eliminate fibroids, maintaining a healthy weight, eating a balanced diet rich in fruits and vegetables, and regular exercise may help reduce symptom severity.
What Happens if Fibroids Go Untreated?
Leaving fibroids untreated can lead to significant complications over time. The most common issues include:
> Severe anemia: Due to prolonged heavy bleeding.
> Chronic pain: Caused by pressure on the pelvis or surrounding organs.
> Bladder and bowel issues: Such as frequent urination, constipation, or urinary retention.
> Infertility: Fibroids can distort the uterine cavity, hindering implantation or causing miscarriages.
In rare cases, rapid fibroid growth or unusual changes may indicate malignancy, making early diagnosis and treatment essential.
Conclusion
Uterine fibroids are common but can lead to serious health issues if left untreated. Recognizing symptoms early, understanding the causes, and exploring available treatments are essential steps in protecting your reproductive and overall health.
While some fibroids may not require immediate intervention, regular check-ups with a gynecologist ensure timely detection and management. Don’t wait until complications arise—addressing fibroids proactively can improve quality of life, fertility outcomes, and long-term well-being.